Knowledge Base
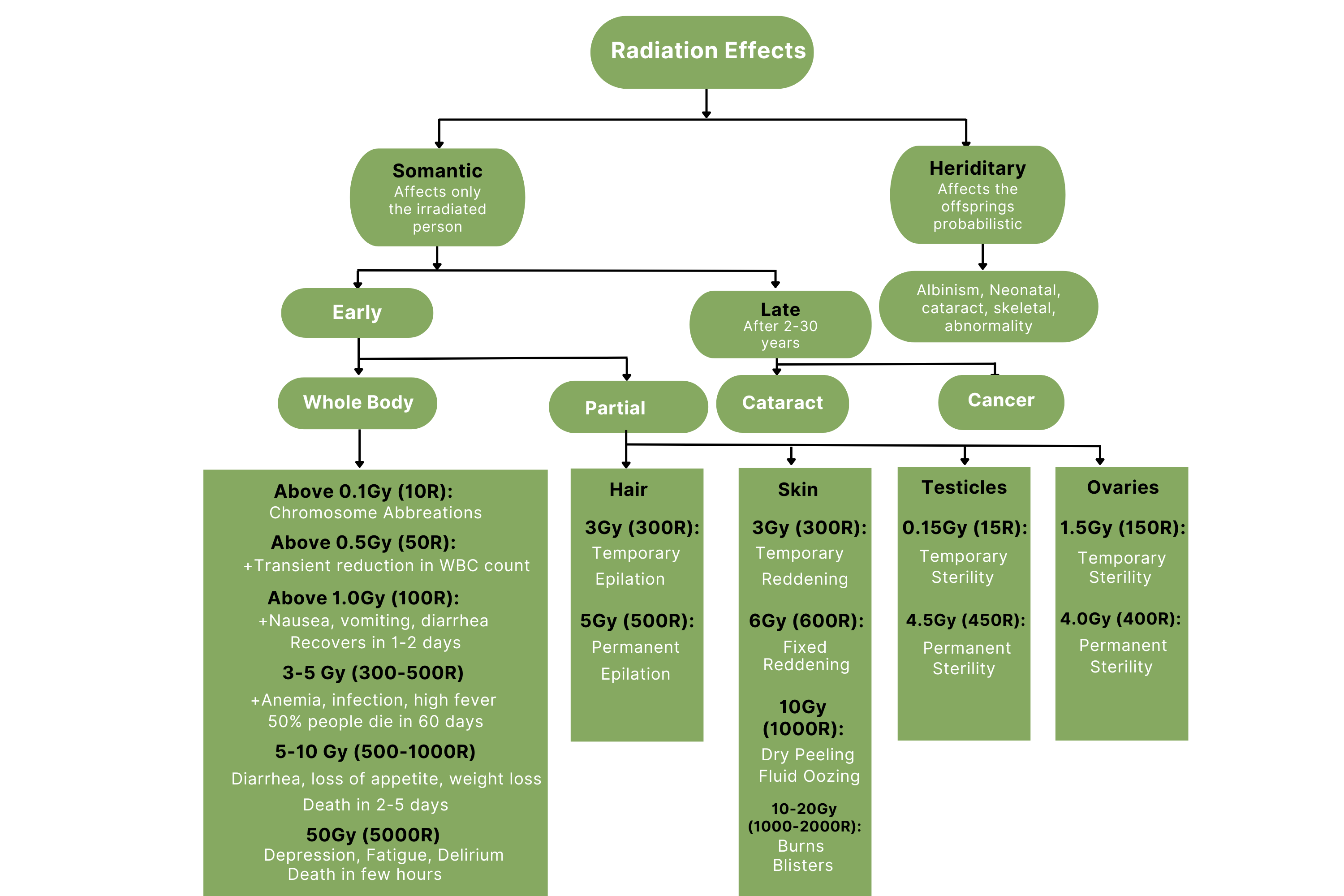
Biological Effects of Radiation in Man :
The effects of nuclear radiation in man are due to its energy absorbed in verious tissue, which is called dose. The effects depend on dose absorbed, the rate at which it is absorbed, type of radiation, strength of radiation & type of tissue.
Dose Limits Recommended by ICRP(1991):
Dose Limits :
| Application |
Dose limit |
|
|
Occupational |
Public |
| Whole Body: |
20mSv (2R) per year, averaged over a defined period of 5 Yrs., with not more than 50mSv(5R) in a single year |
1mSv(100mR) in a year, averaged over 5 years |
| Parts of body(equivalent dose): |
|
|
| Lense of the Eye |
10mSv(15R) per year |
15mSv(1.5R) in a year |
| Skin* |
500mSv(50R) per year |
50mSv(5R) in a year |
| Hands & Feet |
500mSv (50R) per year |
Note: Absorbed dose is measured in Gy or rad (1G = 100rad) & tissue equivalent absorbed dose is measured in Sv or rem (1Sv = 100rem). However, in case of c / g radiation , practically there is not much difference between R, Rad & Rem for tissues. So for understanding purpose, above data is given in R with 1Gy= 100R, an approximate relation.